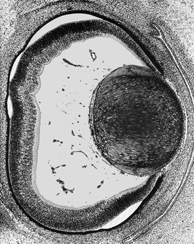
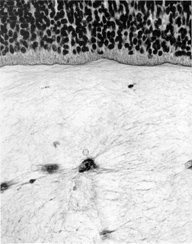
General view of eye at end of embryonic period proper. The primary vitreous body, the scleral condensation and the fornices of the conjunctiva can be seen.
.
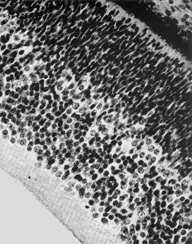
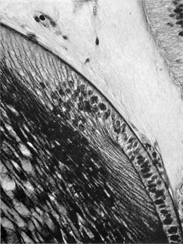
Retina. Internal to the pigmented stratum, the following layers can be seen: proliferative zone and external neuroblastic layer, internal neuroblastic layer, nerve fiber layer and internal limiting membrane.
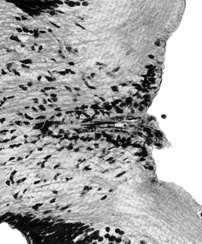
Optic disc. The nerve fibers can be seen passing backward. The point of exit of the hyaloid artery is surrounded by a clump of cells known as Bergmeister's papilla.
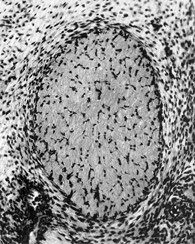
Optic nerve. The stalk now consists almost entirely of nerve fibers. A cellular sheath is evident.
Vitreous body. Indications of the secondary or definitive vitreous body are present adjacent to the internal limiting membrane of the retina.